WGU D080 OA Study Guide I - 2025 | Introduction to Managing in a Global Business Environment📖
Picture this: It’s now possible to think of yourself as a ship captain operating on the open and ever-changing waters of business globally. You must choose where to moor (Greenfield or Brownfield investment) how and with what structures to staff and manage the venture (organizational structure), and who has decision-making authority (centrality versus decentralization). Sounds overwhelming? No sweat here! We’re going to make it as easy – and as fun – as following a treasure map.
In this article, we’ll embark on an exciting journey through three key topics from the WGU D080 module:
- Greenfield and Brownfield Foreign Direct Investments (FDI),
- Four types of organizational structures, and
- Centralized versus decentralized decision-making methods
Think of this as your ultimate survival guide for mastering these concepts. Whether you’re preparing for those tricky WGU D080 OA questions or just curious about how global businesses operate, this guide will help you understand the why, what, and how of these essential topics.
So sit back (or put on your captain’s hat) while we navigate the seas of how companies choose where to spend their money, how they set up their teams, and who gets the last word. By the end, you will be not only passing your WGU D080 module with flying colors but also analyzing the world of business from a completely different perspective. Let’s set sail!
How to Use This Guide for the WGU D080 OA Exam?📖
The D080 Managing in a Global Business Environment OA exam at WGU evaluates your understanding of foreign direct investment strategies, organizational structures, and decision-making methods. This guide simplifies the key concepts of greenfield and brownfield FDI, four types of organizational structures, and centralized vs. decentralized decision-making methods to help you grasp the topics tested in the exam.
We also provide exam-style questions and practical applications to ensure you’re fully prepared for the questions on the WGU D080 OA exam.

Understanding Greenfield and Brownfield FDI: A Beginner’s Guide For D080 OA📝
Another big topic that anyone gets into when studying the WGU D080 module is the distinctions between the Greenfield and Brownfield FDI. Try to recall a game where people are building towns, such as the Sims City game. You have two choices: Begin a game from nothing that is from an untouched plain or make an existing city become better. These choices are very much like the options when firms decide to venture into a new country. Let’s break down the two options: Greenfield and Brownfield Foreign Direct Investment.
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) happens when a company or individual from one country invests in another country. This isn’t just about sending money—it often means owning or controlling businesses or assets in another country. Think of it as a company saying, “I’m ready to build or grow something here!”
FDI comes in two main types:
- Greenfield Investment — Starting something new.
- Brownfield Investment — Improving something that already exists.
Greenfield Investment: Starting Fresh
Greenfield Investment means building everything from the ground up in a foreign country. Imagine you’re building a factory or office on empty land, creating something entirely new.
Key Features of Greenfield Investments:
- High Control: Companies get to design everything their way, from how the buildings look to how the business operates.
- Job Creation: Because everything is new, local personnel are used which is good for the economy.
- Big Investment: There is a lot of time and money spent when it comes to starting a project from the ground. It’s like building a new house – rather costly but fulfilling.
Benefits of Greenfield Investments:
- Economic Growth: The spillover effects include new factories or offices that mean new jobs for people in other countries let alone for people in the host country. Often it can increase local industries, development of skills as well as regional growth.
- Custom Design: Global organizations get an opportunity to apply the latest technological advancement and business practices like sustainable energy, production processes, or up-to-date manufacturing procedures. This gives them a competitive advantage over rivals.
- Long-term Stability: Since they invested in it, companies have stakes in the region and are likely to forge sustainable relations with communities and governments of the region.
Challenges of Greenfield Investments:
- High Costs: Building something new isn’t cheap. Organizations are required to acquire pieces of land, hire construction firms, and install infrastructures which include roads, transport systems, and communication networks.
- Time-Consuming: Construct and plan, one could take a few years to accomplish. For instance, constructing a factory would be much more than the establishment of structures but includes acquisitions of permits, human resource development for the factory workers, and the development of supply channels.
- Regulations: It is also important to consider that local legislation, for example in the area of environmental protection or labor protection legislation, may be very rigid, and a company may need a lot of legal assistance in order to navigate the legislation.
Brownfield Investment: Upgrading What’s There
Brownfield Investment is like moving into an old house and fixing it up. Companies buy or lease existing factories, buildings, or other facilities and make them their own.
Key Features of Brownfield Investments:
- Lower Initial Costs: Since the building or structure already exists, companies don’t have to start from scratch. This reduces expenses on land acquisition and construction.
- Faster Setup: With the basics already in place, businesses can often start operations more quickly. For example, an old factory might only need minor upgrades before production can begin.
- Environmental Concerns: Sometimes, old facilities have problems like pollution or damage that need to be fixed. This can involve significant cleanup and compliance efforts.
Benefits of Brownfield Investments:
- Cost Efficiency: Using existing structures saves time and money, making it an attractive option for businesses looking for quick returns on investment. Companies can often allocate more budget to equipment and training.
- Revitalization: These projects when can revitalize the areas that have long been overlooked for instance the industrial areas or even the urban areas. It may also radically support protecting historic physical assets by redesigning them.
- Reduced Environmental Footprint: Companies who rely on old buildings also reach the goal of constructing new buildings, which in turn reduces the amount of waste products left in the environment. This approach gets into the themes of sustainability.
Challenges of Brownfield Investments:
- Regulatory Issues: Old facilities may not meet modern safety or environmental standards. For example, a factory built decades ago might require updates to comply with current energy efficiency or waste disposal regulations.
- Hidden Costs: Fixing old problems, like cleaning up pollution, can be expensive. For instance, contaminated soil or asbestos in buildings can lead to significant remediation costs.
- Less Control: Since the facilities weren’t built by the company, there might be limitations on how they can be changed. Companies may have to work around existing layouts or structural constraints.
Greenfield vs. Brownfield: A Comparison
Aspect | Greenfield Investment | Brownfield Investment |
Control | Full control over operations | Moderate control, depending on existing conditions |
Costs | High initial costs | Generally lower initial costs |
Time to Market | Longer due to construction time | Shorter; quicker market entry |
Economic Impact | Creates new jobs | Retains or revitalizes existing jobs |
Regulatory Challenges | Fewer initial hurdles | Complex due to potential cleanup requirements |
Real-World Examples
- Greenfield Investment: Imagine a major car company like Tesla building a new factory in another country. This factory brings new jobs, and new technology, and boosts the local economy.
- Brownfield Investment: Think about an old industrial site being purchased and transformed into a modern shopping mall. This gives the area a fresh purpose while using existing resources.
Why Does This Matter?
Greenfield and Brownfield Investments are critical concepts that should interest any business venture planning its globalization strategies. They all have their benefits and issues, and depending on that, we have to select the one that is most appropriate for the company in question, taking into account its objectives, available capital, and, not least, the conditions of the host country.
Quick Tips For D080 OA
If you’re preparing for your WGU D080 OA questions, focus on:
- The key differences between Greenfield and Brownfield investments.
- Examples of when each type might be the better choice.
- The benefits and challenges associated with both types of investments.
These are some concepts you have to grasp to succeed when you take the WGU D080 module and be very prepared for actual business cases.
Up Next: Understanding Organizational Structures
Now that you’ve grasped the basics of Greenfield and Brownfield investments, let’s explore how businesses organize themselves to operate effectively. In the next section, we’ll dive into the four types of organizational structures, breaking them down step-by-step to make them easy to understand.
Understanding the Four Types of Organizational Structures For D080 OA📝
As you continue your journey through the WGU D080 module, understanding the four main types of organizational structures is crucial for learning how businesses are set up to operate effectively. These structures impact everything from how decisions are made to how employees interact and collaborate. Let’s break down these structures step by step, in a way that’s simple and easy to grasp.
Organizational Structures at a Glance
Structure | What It Is | Key Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Functional | Organizes employees by specialized roles or departments, such as marketing, finance, or HR. | Group employees by specific skills or roles, such as marketing, finance, or HR. | Promotes expertise and efficiency within departments. | Can create silos and limit inter-departmental collaboration. |
Divisional | Divides the company based on products, services, markets, or geographical areas. | Teams are grouped based on products, services, markets, or geographical regions. | Faster decision-making and clearer accountability for profits and losses. | Resource duplication and potential competition between divisions. |
Matrix | Combines elements of functional and divisional structures, allowing employees to report to multiple managers. | Combines functional and divisional structures, allowing employees to report to multiple managers (e.g., functional and project). | Flexibility in resource allocation and enhanced collaboration across teams. | Complex reporting relationships and potential for manager conflicts. |
Flatarchy | A hybrid approach that blends flat and hierarchical structures, reducing management layers and empowering employees. | Reduces management layers, creating a more decentralized approach with employee involvement in decision-making processes. | Encourages innovation and quick responses to changes in the market. | This may lead to ambiguity in roles and responsibilities; and struggles with scalability as organizations grow. |
Real-World Examples
- Functional Structure: Coca-Cola, where each department focuses on a specific function, like marketing or production.
- Divisional Structure: Johnson & Johnson, with divisions for consumer products, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices.
- Matrix Structure: NASA, combines technical expertise with project-based missions.
- Flatarchy Structure: Startups like Google in its early days, fostered a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Why Does This Matter?
Understanding these structures helps businesses organize effectively to meet their goals. Each structure has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on the company’s size, industry, and strategy.
Quick Tips For D080 OA
If you’re tackling WGU D080 OA questions, focus on:
- The unique characteristics of each structure.
- How advantages and disadvantages impact business operations.
- Real-world examples that illustrate these concepts.
By mastering these structures, you’ll gain insights into how organizations adapt to thrive in a global business environment.
Up Next: Centralized vs. Decentralized Decision-Making Methods
Now that you understand how businesses organize themselves, the next step is learning how decisions are made within these structures. In the following section, we’ll explore Centralized vs. Decentralized Decision-Making Methods, comparing their benefits and challenges to help you understand their role in global business management.
Tired of reading blog articles?
Let’s Watch Our Free WGU D080 Practice Questions Video Below!
Centralized vs. Decentralized Decision-Making Methods: A Clear Breakdown For D080 OA 📖
In the WGU D080 module, one essential topic is understanding the difference between centralized and decentralized decision-making methods. These approaches dictate how decisions are made within an organization, influencing efficiency, employee involvement, and adaptability. Let’s delve into these concepts step by step in a conversational and structured way.
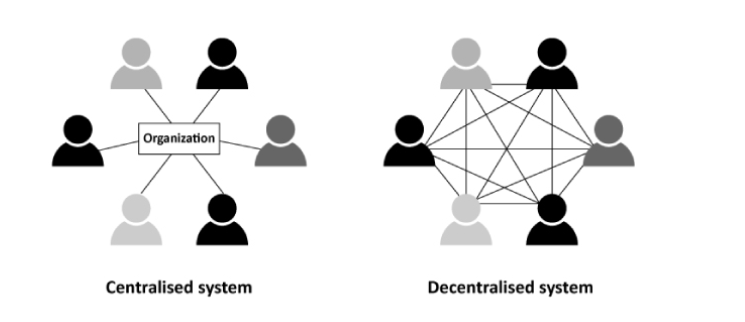
What Are Centralized and Decentralized Decision-Making Methods?
Imagine a company as a tree. In a centralized decision-making structure, all the decisions are made at the top of the tree by a few people at the top management level. These decisions run along the trunk and into the branch (departments). On the other hand, a decentralized organization structure is like a forest in which each tree is a team/department of its own and can make its own decisions.
This is because centralized decision-making concentrates decision-makers at the high levels of management. It ensures that due and proper decisions are taken at an organizational level and are done systematically. Conversely, centralized decision-making permits teams or departments at different tiers within the organization to assume control and bring decentralization and moreover-expeditious response to change.
Comparison of Centralized and Decentralized Methods
Aspect | Centralized Decision-Making | Decentralized Decision-Making |
Authority | Concentrated at the top levels of management. | Distributed among various levels and departments. |
Communication | Flows in a vertical, top-down hierarchy. | Encourages horizontal and flexible communication channels. |
Decision Speed | Can be slower due to bureaucratic processes. | Typically faster as fewer approvals are required. |
Employee Role | Limited input from lower levels. | Encourages autonomy and empowers employees. |
Consistency | Ensures uniformity in decisions across the organization. | Decisions may vary between departments, leading to potential inconsistencies. |
Adaptability | Struggles to adapt quickly in dynamic environments. | Highly adaptable, especially in changing markets or diverse operations. |
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Centralized Decision-Making
In general, the centralized decision-making approach is good because it guarantees uniform management of the organization. So let us take the example of a company such as Apple – famous for cohesively distinctive product designs – that uses centralized control. Corporate-level management takes a central role in product planning and promotion while guaranteeing all the strategies fit the company’s mission.
Advantages:
- Ensures consistency and uniformity in decisions across the organization.
- Facilitates control and compliance in stable or regulated environments.
- Reduces task duplication by maintaining clear leadership.
Disadvantages:
- Slower decision-making due to reliance on a few individuals.
- Employees may feel excluded, leading to low motivation.
- Lacks flexibility in dynamic or rapidly changing environments.
Decentralized Decision-Making
It is most effective in settings that demand flexibility, the organizational structure of decentralized decision-making is the best. For example, Unilever allows its regional offices to make local choices in reaction to buyer preferences. This is especially important for a global organization that is doing business in various markets since it provides a proper response to the needs of customers.
Advantages:
- Enhances responsiveness to local needs and market changes.
- Boosts employee engagement by promoting autonomy.
- Encourages innovation and creativity within teams.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of inconsistent decisions across departments.
- Potential for conflicts among stakeholders making independent decisions.
- Requires significant training and resources to empower decision-makers effectively.
When to Use Each Method
The choice between centralization and decentralization depends on the company’s needs:
- Centralized Decision-Making is ideal for:
- Small organizations where consistency and control are critical.
- Stable environments require strict compliance or risk management.
- Decentralized Decision-Making works best for:
- Large organizations need flexibility to operate in diverse markets.
- Dynamic industries where local expertise and quick responses are crucial.
Real-World Examples
Consider Apple as an example of centralized decision-making. Its tightly controlled processes ensure that every product, from the iPhone to the MacBook, reflects the company’s brand values. On the other hand, Unilever’s decentralized approach allows its teams in different countries to tailor products and marketing strategies to local markets, making it more effective in diverse regions.
Why Is This Important?
The outlines of centralized and decentralized decision-making assist in differentiating between the two and determining which one should be adopted depending on size, type of company, or business goals. This is the fine line between control and flexibility, which is commonly at the heart of organizational capability to respond to threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Quick Tips For D080 OA
If you’re preparing for WGU D080 OA questions, focus on:
- How centralized structures ensure consistency and compliance.
- Why decentralized structures foster innovation and responsiveness.
- Real-world examples that illustrate these approaches in action.
By grasping these concepts, you’ll be ready to analyze decision-making strategies in real-world scenarios, giving you an edge in both exams and professional applications.
Conclusion: Anchoring Your Understanding of Global Business with WGU D080 OA Insights📖
Congratulations! You have let the ships sail through Greenfield and Brownfield investments, identified the internal structures of organizations, and grappled with centralized structure and decentralized structures for business decisions. Some of these focal ideas from the WGU D080 module are not academic figments of imagination; they are the map for direction in ‘real-life’ business plans.
By understanding where to invest, how to organize, and who makes the calls, you’ve equipped yourself with valuable tools to tackle global business challenges. Whether you’re aiming to ace those WGU D080 OA questions or aspiring to lead in the business world, these insights will serve you well.
Remember, success in managing global environments is all about balance. Knowing when to centralize or decentralize, how to structure for efficiency, and where to invest for growth can turn challenges into opportunities. So, take these lessons, put on your captain’s hat, and steer your ship confidently into the vast ocean of global business opportunities. Bon voyage!