WGU C215 OA Study Guide - 2025 | A Guide to Project Management, Just-In-Time, and Quality Control 📖
Ever feel like managing a project is like juggling flaming torches while riding a unicycle? Or that keeping an inventory under control is like guessing how much pizza your friends will eat at a party? Well, that’s where operations management comes in! Whether you’re a student preparing for WGU C215 OA or a business professional looking to optimize workflows, mastering these key principles will make your life a whole lot easier.
In this guide, we’ll explore three fundamental topics that are essential for efficiency in any business:
- Project Management Lifecycle – The roadmap that takes a project from concept to completion.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) – The inventory strategy that ensures you have just what you need, exactly when you need it—no more, no less.
- Quality Management and Problem-Solving Tools – The techniques that maintain production efficiency while delivering superior products and services to customers.
Identifying these principles helps employees evacuate hard work in exchange for working intelligently. Operations management principles enable businesses to reduce waste and boost both process effectiveness and customer satisfaction through their guiding principles of planning and execution and continuous improvement cycles.
This article explores critical topics broken down in an approachable manner which also includes a touch of excitement.
How to Use This Guide for the WGU C215 OA Exam?📖
The C215 Operations Management OA exam at WGU evaluates your understanding of project management, inventory management, and quality control. This guide simplifies the key concepts of the project management lifecycle, JIT (Just-In-Time), and quality management and problem-solving tools (Pareto, Fishbone, Histogram, etc.) to help you grasp the topics tested in the exam.
We also provide exam-style questions and practical applications to ensure you’re fully prepared for the questions on the WGU C215 OA exam.

Project Management Lifecycle: A Step-by-Step Guide For C215 OA📝
A project management process mirrors the process of planning an extensive journey. Being prepared for tests such as WGU C215 OA or leading practical projects requires a complete understanding of structured project management principles. On any trip, you need to establish where you will go as well as how much you need to spend before you can start packing. The process of project management requires a step-by-step approach to maintain smooth operations between starting and ending points. The structured management process known as Project Management Lifecycle extends across five stages beginning with Initiation and finishing with Closure. Every project phase exists to maintain projects within their budget and goals while keeping all activities on schedule.
Understanding the Project Management Lifecycle
Developing projects becomes simpler through the Project Management Lifecycle because it offers an organized framework that lets teams maintain their structure and successfully achieve their objectives. The five phases function as guidance for managers who start their work in idea formation all the way to completion.
The five key phases include:
Phase | Purpose |
Initiation | Define project scope, feasibility, and goals |
Planning | Develop a detailed project roadmap |
Execution | Carry out project tasks and manage resources |
Monitoring & Controlling | Track progress and make adjustments |
Closure | Finalize project and evaluate outcomes |
Each phase is crucial to ensuring a successful project, and skipping any step could lead to inefficiencies and project failures. Let’s take a closer look at each phase.
1. Initiation: Laying the Foundation
Constructing a house requires rock-solid foundations before construction starts. During the project initiation phase, essential components get established which include purpose identification scope definition, and feasibility assessment. During this initial phase, project implementation decisions are made while stakeholders receive proper alignment for project execution.
A few key tasks in this phase include:
- Creating a project charter – This document outlines the project’s goals, scope, and stakeholders.
- Conducting a feasibility study – Helps determine if the project is achievable within time, budget, and resource constraints.
- Developing a business case – Justifies why the project should be undertaken and what value it will bring.
- Identifying stakeholders – Knowing who is involved and what their expectations are helps in smooth communication and collaboration.
Weakly defined project objectives stand as a main obstacle during this phase. A project starts to veer away from its direction as soon as goals remain undefined thus causing both confusion and scope expansion. Insufficient stakeholder involvement creates misunderstandings between parties because their expectations may not match.
2. Planning: Mapping Out the Details
After approval of a project teams must develop an extensive plan for execution. The team uses this step to develop a comprehensive pathway that will lead them to project success. A project that lacks proper planning will deviate from the path which leads to unsuccessful completion along with delays in delivery and excessive spending.
Key aspects of this phase include:
- Developing a project plan – Includes timelines, tasks, and resource allocations.
- Defining milestones – Setting checkpoints to track progress.
- Scheduling tasks – Assigning deadlines and time estimates.
- Outlining risk management strategies – Identifying potential risks early for proactive solutions.
- Establishing communication protocols – Ensuring smooth collaboration among team members.
A well-structured plan is like a blueprint, keeping the team focused and preventing unnecessary delays.
3. Execution: Bringing the Plan to Life
This is where the action happens! The execution phase is all about bringing the project plan to life. Here, tasks outlined in the planning phase are implemented to create the desired outcome.
During execution, project managers focus on:
- Allocating resources – Ensuring the right people, tools, and materials are in place.
- Managing team coordination – Keeping everyone aligned with project objectives.
- Implementing the project plan – Executing tasks while ensuring quality and efficiency.
A major challenge during this phase is maintaining team efficiency. Effective leadership and clear communication play a crucial role in keeping the team motivated and avoiding delays.
4. Monitoring and Controlling: Keeping Everything on Track
Even with a solid plan, things don’t always go as expected. The monitoring and controlling phase ensures the project stays on course by identifying deviations and making necessary adjustments.
In this phase, project managers:
- Track project progress – Regularly check if tasks are completed on time.
- Measure performance using KPIs – Key Performance Indicators help assess project success.
- Address deviations from the plan – Adjust budgets, timelines, or resources as needed.
By closely monitoring progress, managers can take corrective actions before small issues turn into big problems.
5. Closure: Wrapping It All Up
The final stage represents the project’s completion point which involves work review and official wrapping up of the project together with its details. A project reaches true success only when proper closure procedures are completed.
Steps in this phase include:
- Obtaining client approval – Ensuring the final deliverable meets expectations.
- Settling contracts and payments – Closing all financial aspects of the project.
- Conducting a post-project review – Evaluating successes, challenges, and lessons learned.
- Communicating completion to stakeholders – Keeping everyone informed about the project’s conclusion.
A well-structured closure ensures all loose ends are tied up, and valuable insights are documented for future projects.
We have established our understanding of project management phases yet we should analyze the revolutionary approach of Just-In-Time (JIT) because this concept is essential for those who need WGU C215 OA question preparation.
Just-In-Time (JIT): A Lean Approach to Efficiency For C215 OA 📝
The fast-moving environment within modern business production requires organizations to find precise equilibrium points between product delivery speed and resource utilization reduction. Just-In-Time (JIT) introduces a production strategy that optimizes efficiency through exact material delivery requirements and reduces inventory costs and supports improved operational flow. Learning the principles of Just-In-Time (JIT) remains essential for professionals who work in lean production regardless of their WGU C215 OA examination activities.

What is Just-In-Time (JIT)?
JIT stands as a lean manufacturing method geared toward waste reduction by creating products only during times of product demand. With JIT businesses do not maintain large reserves of raw materials and finished goods because they deliver and make products only in response to direct customer requirements.
Simply stated JIT operates on three fundamental principles which include the elimination of waste together with efficient operation and fast demand responsiveness. The system needs both supplier and production team coordination as well as advanced customer demand analysis.
Key Principles of JIT:
- Demand-driven production: Items are produced only when orders are received.
- Minimal inventory: Reducing excess raw materials and finished goods.
- Continuous improvement: Refining processes to eliminate inefficiencies.
- Strong supplier relationships: Ensuring a steady and reliable flow of materials.
Benefits of Implementing JIT
Companies that successfully implement JIT can enjoy significant advantages in their production systems. Here are some key benefits:
Benefit | How It Helps |
Waste Reduction | Minimizes excess inventory and overproduction, reducing storage costs. |
Lower Operational Costs | Less capital is tied up in unused materials, improving cash flow. |
Improved Efficiency | Streamlined workflows and reduced idle time boost productivity. |
Better Quality Control | Focus on smaller, manageable production batches improves quality checks. |
Faster Response to Demand | Companies can quickly adjust production based on real-time market needs. |
Lower Storage Requirements | Less warehouse space needed, reducing overhead costs. |
By integrating JIT into their operations, businesses can remain agile and competitive, ensuring resources are utilized effectively.
Challenges of JIT Implementation
While JIT offers numerous advantages, implementing it requires overcoming several hurdles:
- Supplier Reliability: Since JIT relies on timely deliveries, any disruption in the supply chain can halt production.
- Demand Variability: Sudden spikes in customer demand can challenge JIT systems if they aren’t flexible enough.
- Strict Quality Control: Defects in production can cause major delays since there’s no surplus inventory to fall back on.
- Initial Implementation Costs: Setting up a JIT system requires investment in logistics, technology, and training.
To counter these challenges, businesses must build strong supplier partnerships, use data-driven demand forecasting, and maintain rigorous quality control measures.
JIT and Other Operations Management Strategies
JIT isn’t an isolated concept—it integrates seamlessly with other operations management strategies to enhance efficiency:
- Lean Manufacturing: JIT is a core component of lean principles, helping eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Since JIT minimizes buffer stock, quality control must be stringent to prevent defects.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): JIT requires a well-managed supply chain for smooth material flow.
- Demand Forecasting: Using real-time data, JIT ensures production aligns with actual rather than predicted demand.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): JIT integrates with ERP systems to automate material ordering and inventory tracking.
Companies that combine JIT with these strategies can build resilient, efficient, and customer-centric production systems.
Building on the efficiency of JIT, mastering Quality Management and Problem-Solving Tools—including Pareto analysis, fishbone diagrams, and histograms—is essential for ensuring product excellence and process improvements, a key focus of WGU C215 OA questions.
Tired of reading blog articles?
Let’s Watch Our Free WGU C215 Practice Questions Video Below!

Quality Management and Problem-Solving Tools: A Roadmap to Excellence For C215 OA📖
Revenue success for businesses depends on providing top-quality products and services. Quality management supports industries of all types to deliver products that fulfill customer needs while eliminating unwanted resources and performance losses. Quality Management and Problem-Solving Tools constitute essential components for attaining these three objectives. Students who want to succeed on WGU C215 OA questions must understand these tools to maximize their operations management skills.
What is Quality Management?
Quality management serves as a path to monitor products and services in order for them to fulfill predetermined benchmarks. This system works through ongoing development along with defect avoidance systems which lead to customer contentment. Quality management consists of three core principles beginning with Total Quality Management (TQM) and extending to statistical quality control (SQC) together with multiple problem-solving tools.
Key Aspects of Quality Management:
- Total Quality Management (TQM): A company-wide approach focusing on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- Quality Standards: Industry-specific benchmarks like ISO 9001 ensure consistency in production.
- Six Sigma: A data-driven method for reducing defects and improving processes.
- Cost of Quality: Includes prevention, appraisal, and failure costs to measure quality effectiveness.
Statistical Quality Control (SQC) and Its Role
The application of Statistical Quality Control (SQC) enables companies to enhance and keep their quality standards through statistical analysis methods. The functions of SQC maintain processes within specific boundaries which enables defect prevention before any failures occur.
Key Concepts in SQC:
- Common vs. Assignable Causes of Variation: Understanding whether variations in a process are natural (common) or due to specific factors (assignable).
- Process Capability Index (Cpk): Measures how well a process can produce within given specifications.
- Six Sigma Approach: A five-step methodology (DMAIC—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to reduce defects and improve efficiency.
Problem-Solving Tools for Quality Management
To identify, analyze, and solve quality-related issues, businesses use a variety of problem-solving tools. Three of the most essential tools are Pareto charts, Fishbone diagrams, and Histograms.
Pareto Chart: Prioritizing Problems

A Pareto chart follows the 80/20 rule, which states that 80% of problems come from 20% of causes. This tool helps organizations prioritize which defects or issues to focus on first.
How Pareto Charts Help in Quality Management:
- Visualizes the most frequent causes of defects.
- Helps managers allocate resources efficiently.
- Supports decision-making by highlighting critical problem areas.
Fishbone Diagram: Identifying Root Causes
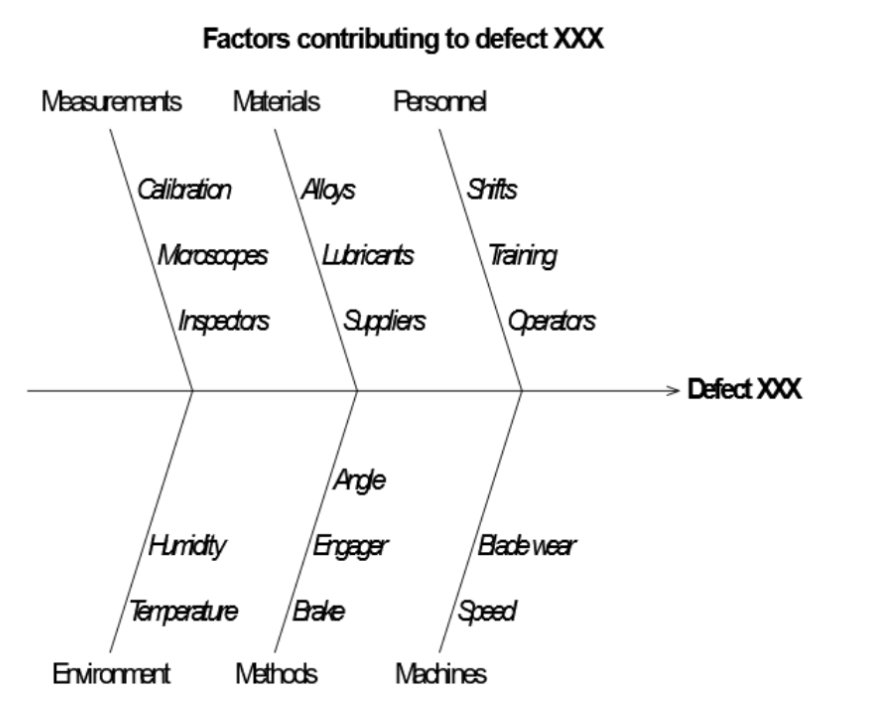
Also known as the Ishikawa Diagram, a Fishbone diagram categorizes possible causes of a problem into groups like People, Methods, Materials, Machines, Measurement, and Environment (the 6Ms).
How Fishbone Diagrams Help:
- Provides a structured way to brainstorm problem causes.
- Helps teams visually map out potential sources of quality issues.
- Encourages collaborative problem-solving.
Histogram: Understanding Process Variability
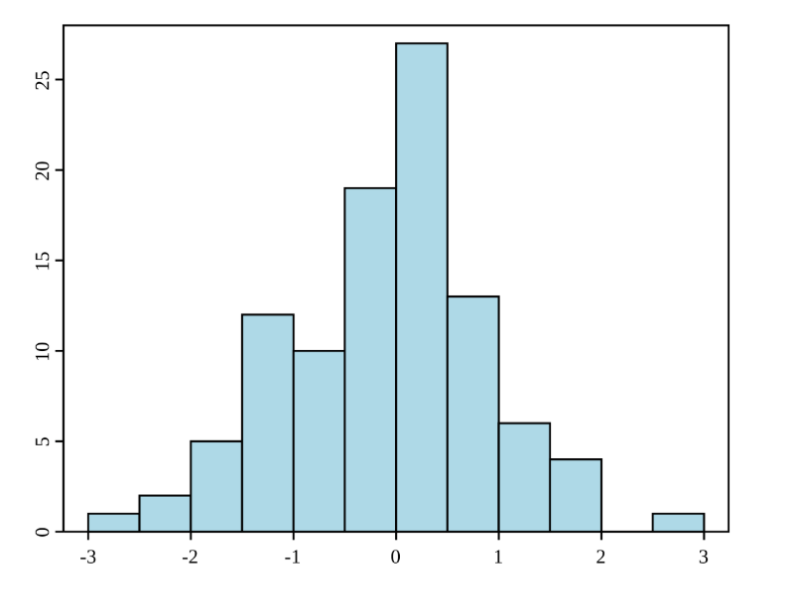
A Histogram is a graphical representation of data distribution, making it easier to identify patterns and variations in a process.
How Histograms Improve Quality:
- Displays process performance over time.
- Highlights defects or inconsistencies.
- Helps businesses adjust processes for greater stability.
Tool | Purpose | Best Used For |
Pareto Chart | Prioritizes the most common issues | Identifying major problem areas |
Fishbone Diagram | Identifies root causes of a problem | Complex quality issues |
Histogram | Analyzes data distribution & process performance | Tracking variations & trends |
How Quality Management Tools Integrate with Other Strategies
Quality management is not a standalone practice—it connects with several operations management strategies for enhanced efficiency:
- Lean Manufacturing: Eliminates waste while maintaining high quality.
- Just-In-Time (JIT): Ensures materials and production align with demand.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): Promotes company-wide focus on quality.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrates quality management with supply chain and business operations.
By incorporating quality management tools into these strategies, businesses can ensure consistent process improvements, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
Final Thoughts: Mastering Operations Management for WGU C215 OA Success 📖
Operations management exists as more than theoretical models since it functions as a useful business framework to maintain operational smoothness. Any organization can achieve success using three essential operational concepts that include efficient project management alongside JIT inventory techniques and problem-solving methods such as Pareto charts and fishbone diagrams.
Students who enroll in WGU C215 OA need to fully understand these management principles. Take special care to review project management along with lean inventory practices and quality control tools since these subjects appear in the final Objective Assessment (OA). Learning these fundamental principles will prepare you to excel on your exam and develop professional skills that you can later use in your career.
Continuous improvement stands as the main objective while efficiency serves as the key and problem-solving functions as your supreme power in operations management. Make sure to practice nonstop and ask questions persistently while you absolutely prioritize success on your WGU C215 OA assessment. You’ve got this!






